The Mountain Nyala of Ethiopia: Can a Single Species Save an Entire Ecosystem? (5-minute Video)
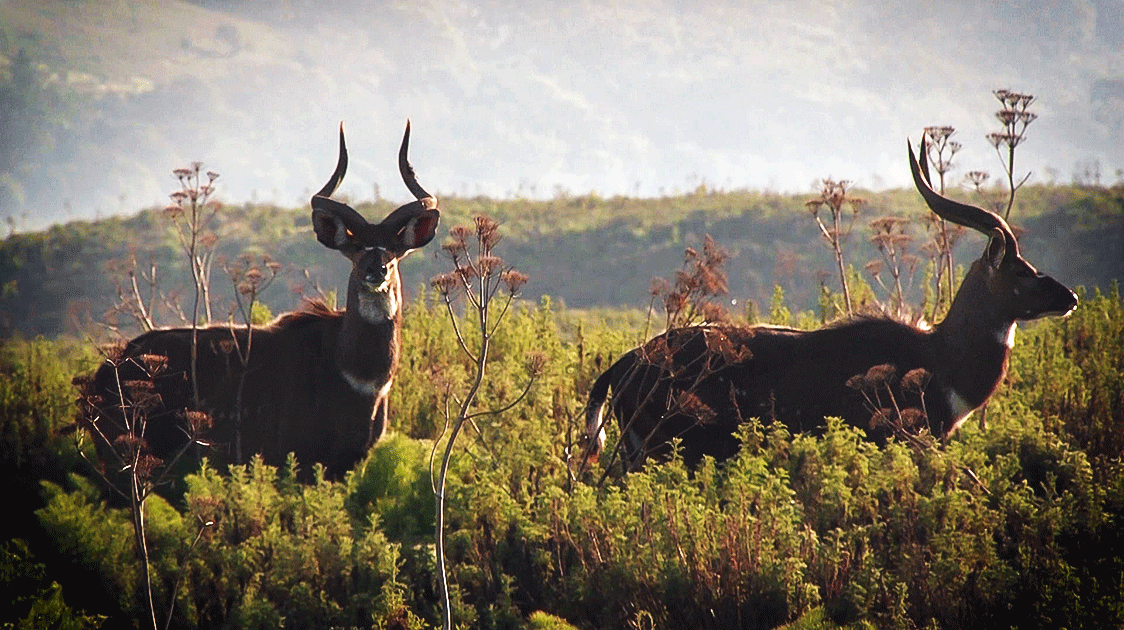
Ethiopia currently has five safari hunting outfitters conducting safaris in remote wilderness areas. Jointly, they are responsible for protecting over 2000 sq. km of Mountain Nyala habitat. Instead of using a government-controlled conservation approach, safari outfitters opted for a different management program utilizing community empowerment. Communities that border Forestry Priority Areas – FPAs agreed to the Participatory Forest Management Program -PFMP
This program allows for controlled, sustainable usage of these FPAs. Hunting operators work hand in hand with communities to protect the FPAs and allow controlled and monitored access. Locals are incentivized to see value in wildlife and the ecosystem.
Villagers are still permitted to conduct traditional lifestyle practices such as collecting honey and dry firewood. Other benefits include 60% of the revenue from concession and hunting fees and much-needed employment as game scouts and safari staff. Regular patrols and a presence by anti-poaching units are held year-round.
Without safari hunting outfitters to implement this program, these FPAs would be decimated.


Comments ()